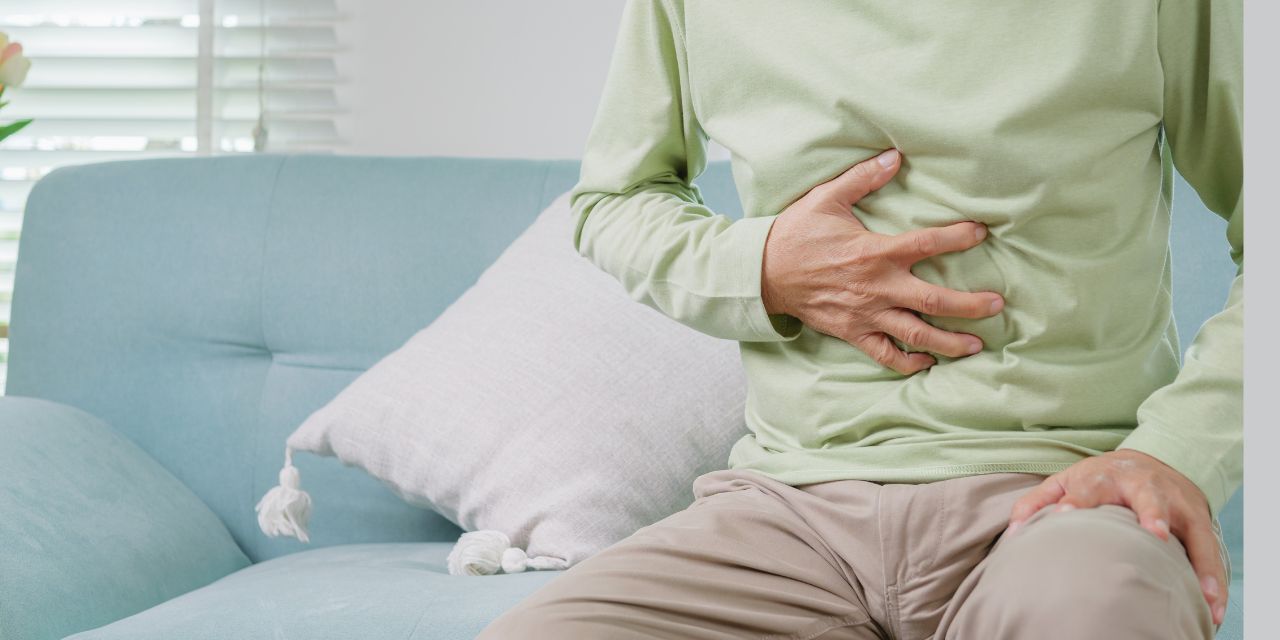
A hernia occurs when an internal part of the body pushes through a weakness in the muscle or surrounding tissue wall. Though hernias can affect anyone, the symptoms, risk factors, and treatments may vary between men and women. In this article, we’ll explore the differences in how hernias manifest in men and women, why these differences exist, and how they influence treatment options.
Types of Hernias
There are several types of hernias that affect both men and women, but the most common ones include:
Inguinal hernia: The most frequent type, occurring in the groin area. It is far more common in men.
Femoral hernia: This type affects the upper thigh near the groin and is more likely to occur in women.
Umbilical hernia: Located around the belly button, this type affects both men and women, particularly during or after pregnancy.
Hiatal hernia: Occurs when part of the stomach pushes up through the diaphragm into the chest, commonly seen in both genders but tends to increase with age.
Anatomical Differences: Why Men and Women Experience Hernias Differently
The reason men and women experience hernias differently stems from anatomical variations. Men have a natural weakness in the abdominal wall due to the passage of the spermatic cord through the inguinal canal. This makes them more susceptible to inguinal Outpouching, which account for about 75% of all hernia cases.
Women, on the other hand, are more likely to experience femoral Outpouching due to the wider shape of the female pelvis. These occur when a portion of the intestine or fatty tissue bulges into the femoral canal. Femoral hernias are less common but tend to be more dangerous due to the increased risk of complications like bowel obstruction or strangulation.
Symptoms of Hernias: Women vs. Men
While Outpouching symptoms are generally similar in both men and women, they can present differently depending on the location and severity of the hernia. Common symptoms include a visible bulge, discomfort, or pain at the site of the Outpouching, especially when lifting, coughing, or standing.
In Men:
Inguinal hernia: Men typically experience a noticeable lump in the groin or scrotum, which may cause a feeling of heaviness or dull ache. The pain may intensify after physical activity or exertion.
Hiatal hernia: Men may experience acid reflux, chest pain, or difficulty swallowing when part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm.
In Women:
Femoral hernia: Women are less likely to notice a visible bulge, but they may experience deep pelvic pain, which can be misdiagnosed as other conditions like ovarian cysts or endometriosis.
Umbilical hernia: Women, especially those who have been pregnant, may notice a bulge near the belly button. This may worsen after pregnancy or due to obesity.
Hiatal hernia: Symptoms are similar to those in men, with complaints of acid reflux, chest discomfort, or difficulty swallowing.
Women may be less likely to receive an accurate diagnosis due to the subtler presentation of hernias. Misdiagnosis is common, as symptoms in women may be mistaken for gynecological conditions or dismissed as gastrointestinal issues. In men, the presence of a visible lump makes it easier to diagnose the hernia correctly.
Risk Factors: Are Men or Women More at Risk?
Men are at a significantly higher risk of developing hernias, particularly inguinal hernias. Studies suggest that up to 27% of men will develop an inguinal hernia during their lifetime, compared to only about 3% of women.
However, women are more prone to femoral hernias, particularly after childbirth or due to chronic conditions like obesity. Pregnancy, especially multiple pregnancies, weakens the abdominal wall and increases the likelihood of umbilical and incisional hernias in women.
Treatment Options: Differences for Men and Women
Hernias typically do not heal on their own, and surgery is often required to prevent complications such as bowel obstruction or strangulation. The type of hernia and its severity will determine the treatment method.
For Men:
Inguinal hernia repair: The most common surgery for men, this procedure involves pushing the hernia back into place and reinforcing the weak spot in the abdominal wall with mesh. It can be performed as open surgery or laparoscopically.
Hiatal hernia repair: If lifestyle changes and medications do not help with symptoms, surgery may be required to repair a hiatal hernia, which may involve pulling the stomach back into the abdomen and reinforcing the diaphragm.
For Women:
Femoral hernia repair: Since femoral hernias in women carry a higher risk of complications, early surgical intervention is critical. Laparoscopic surgery is often used to repair femoral hernias by pushing the intestine or tissue back into place and reinforcing the area with mesh.
Umbilical hernia repair: For women, particularly post-pregnancy, umbilical hernia repair involves a relatively simple procedure, either through open surgery or laparoscopy. This may be combined with other procedures, such as a tummy tuck, for women seeking abdominal reconstruction post-pregnancy.
While both men and women may undergo similar hernia repair surgeries, the surgical approach can differ based on anatomical differences. For example, women undergoing hernia repair may also need surgery for gynecological conditions like endometriosis, which could be contributing to their symptoms.
Recovery and Recurrence
Recovery from hernia surgery is generally similar for both genders, with most patients returning to normal activities within a few weeks. However, women may face longer recovery periods if the hernia is combined with other pelvic or abdominal surgeries. Recurrence rates are generally low for both genders but can be higher in cases of severe hernias or after multiple surgeries.
Conclusion
Understanding hernia symptoms and treatment differences between men and women is vital for effective care. Men commonly develop inguinal hernias with noticeable bulges and discomfort, while women face complications from femoral hernias, which may present subtler symptoms.
For residents seeking hernia treatment in Panchkula, it’s important to recognize risk factors like obesity, advanced age, smoking history, and heavy lifting. Early intervention is crucial to prevent serious complications, such as strangulation.
At Malhotra Hospital & Orthopaedic Centre, we provide tailored care and utilize advanced techniques for optimal hernia repair outcomes. For expert guidance, contact Dr. Sunil Malhotra at +91-730217302 or 0172-2596286. Your health is our priority.